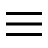To improve overall security when browsing the Internet Google checks all HTTPS certificates, so you can know who certified those sites. To force website administrators to switch to HTTPS, Google marks all sites without encryption (ie in HTTP) as "unsafe".
To improve overall security when browsing the Internet Google checks all HTTPS certificates, so you can know who certified those sites. To force website administrators to switch to HTTPS, Google marks all sites without encryption (ie in HTTP) as "unsafe".Let's find out together what does "Unsafe" mean in Chrome that appears on old sites or sites not updated in HTTP, what we really risk and how we should behave with these sites.
ALSO READ: What to do if the site's SSL security certificate fails
Encrypted pages on the web
One of the major Internet security problems concerns unencrypted web pages, that is, without any active encryption and without a certificate that certifies the validity of this encryption. Put simply it means that all the information that passes between the site and our PC is easily intercepted and can be analyzed with a sniffer: an attacker connects to our own network (perhaps a public hotspot) and starts capturing packets, so as to see which sites we visit and which passwords we enter to access our favorite sites.
This not only leads to privacy concerns but is a danger to our accounts: in the past it was the preferred method for steal Facebook password, since access to the famous site was made on an unencrypted page.
With the push of Google not only sites where passwords are entered, but also simple sites are now protected with HTTPS, so as to protect the connection and avoid the word Not safe on Chrome.
How site encryption works
HTTPS sites encrypt data that are transmitted between the device and their servers, protecting users from cyber attacks. HTTPS also offers another advantage, because it hides the full path of the web pages we visit so that no one, not even our internet provider, will be able to see which page we are reading.
These sites cannot certify themselves "alone", but they need a certificate issued by an independent company specialized in the secure certification of sites (such as COMODO): once the SSL certificate they will result as safe on all browsers, since the company will always verify the identity of the owner of the site (or of the company that owns it) before issuing a certificate.
In fact, "self-made" certificates are not considered safe by Chrome, which will still show a warning window even if we use HTTPS (in this case we speak of non-validated encryption).
How to recognize unsafe sites?
When you open a site that starts with HTTP, Chrome marks it with the inscription Not sure visible at the top left of the address bar.
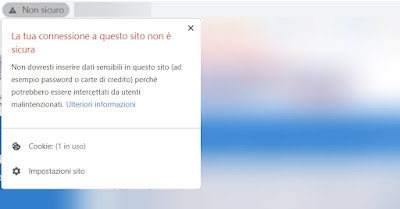 Chrome is telling us that the connection is not secure because there is no encryption for connecting to the site. Everything is sent over the connection in visible text, which means it is vulnerable to snooping and tampering.
Chrome is telling us that the connection is not secure because there is no encryption for connecting to the site. Everything is sent over the connection in visible text, which means it is vulnerable to snooping and tampering.If we happen to be on such a site it is better to go out or, if we really can't avoid it, we absolutely avoid writing private information such as passwords or payment details on a website of this type: the risk of wiretapping is very high.
An unencrypted website is also vulnerable to tampering, in fact, someone expert could modify the data that the site shows us by carrying out an attack Man-In-The-Middle.
How to force a secure connection
So if we happen to be on an HTTP site we don't always have to run away: it can still be harmless and harmless as it was until a few months ago, the important thing is not to send personal data to the site, not to log in and write passwords. If possible, we personally change the web address and add https instead of http: if a site has a valid certificate vthe secure page will load and we will avoid the unencrypted page (which often remains visible because it is indexed by Google).
Those who want to make sure they only browse HTTPS sites can install the popular extension HTTPS Everywhere on Chrome and Firefox browsers, which always forces the opening of protected pages and significantly increases the security of the browser and the connection.
Conclusions
The encrypted connection of websites has made it much more difficult to steal login credentials and spy on users within the public network, but the encrypted connection alone is not sufficient to prevent possible violations related to DNS requests (which are often in the clear , therefore within everyone's reach) or violations related to the replacement of web pages.
To be on the safe side, we can increase the security level always using a VPN when we are connected to a public Wi-Fi and, to prevent cyber attacks, it is advisable to have one good antivirus with network scanning module.
Let's not forget about always keep your browser updated: this is the only way we can always get the right warning when we encounter an unsafe site and always have security updates for the browser components.